GET基本流程
GET是根据index、type和ID向ES发送请求,获取文档数据,是读取操作,因此主分片或者副本分片都可以返回文档,不过新增的文档已经写入到主分片中但是还没有复制到副本分片时,副本分片可能会报告文档不存在。
假设有三个节点,分别存储着分片0和分片1,P开头的为主分片,R开头的为副本分片:
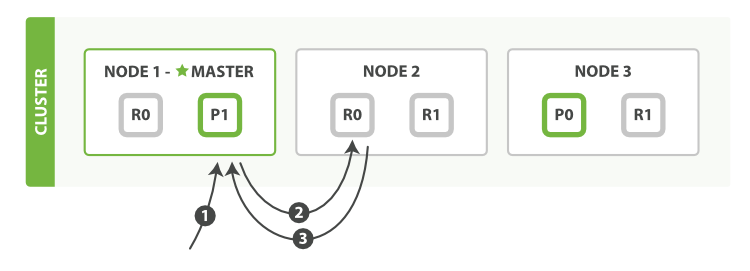
1.客户端向节点1发送GET请求
2.节点根据文档的ID判断文档属于哪个分片,这里假设文档属于分片0,通过集群状态中的内容路由表得知三个节点Node1、Node2、Node3中都含有分片0,此时节点1可以将请求发送给任意节点,假设发给了节点2
3.节点2根据ID从分片0上获取文档,然后将文档返回给节点1,由节点1返回给客户端
源码分析
协调节点
1.路由
- 首先获取集群状态、节点列表等信息
- 根据路由算法(或者是请求参数中指定的优先级和集群状态确定)获取文档所在的分片,因为分片可能存在副本,因此得到的是一个列表
TransportSingleShardAction
TransportSingleShardAction.AsyncSingleAction的构造函数中,准备集群状态、节点列表等信息,并计算文档所在分片:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45public abstract class TransportSingleShardAction<Request extends SingleShardRequest<Request>, Response extends ActionResponse> extends TransportAction<Request, Response> {
class AsyncSingleAction {
private final ActionListener<Response> listener;
private final ShardsIterator shardIt;
private final InternalRequest internalRequest;
private final DiscoveryNodes nodes;
private volatile Exception lastFailure;
private AsyncSingleAction(Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener) {
this.listener = listener;
// 集群状态
ClusterState clusterState = clusterService.state();
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("executing [{}] based on cluster state version [{}]", request, clusterState.version());
}
// 集群中的节点列表
nodes = clusterState.nodes();
ClusterBlockException blockException = checkGlobalBlock(clusterState);
if (blockException != null) {
throw blockException;
}
String concreteSingleIndex;
if (resolveIndex(request)) {
// 获取索引名称
concreteSingleIndex = indexNameExpressionResolver.concreteSingleIndex(clusterState, request).getName();
} else {
concreteSingleIndex = request.index();
}
// 创建InternalRequest对象
this.internalRequest = new InternalRequest(request, concreteSingleIndex);
// 解析请求
resolveRequest(clusterState, internalRequest);
blockException = checkRequestBlock(clusterState, internalRequest);
if (blockException != null) {
throw blockException;
}
// 根据路由算法得到文档属于哪个shard,或者根据请求中设置的参数选择,因为分片可能存在多个副本,因此得到的是一个迭代器
this.shardIt = shards(clusterState, internalRequest);
}
}
}
2.转发
- 根据分片所在的节点ID从集群中的节点列表获取该节点,得到目标节点
调用TransportService的sendRequest方法向目标节点转发请求,在转发之前判断本机节点是否是目标节点:
(1)如果本机节点是目标节点,返回的连接是localNodeConnection,进入TransportService的sendLocalRequest流程
(2)如果本机节点不是目标节点,返回一个连接目标节点的Connection,然后异步发送请求到网络,等待处理的Response
- 等待数据节点的回复,如果数据节点处理成功,返回给客户端,如果处理失败进行重试
TransportSingleShardAction
TransportSingleShardAction.AsyncSingleAction的perform方法向目标节点转发请求:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48private void perform(@Nullable final Exception currentFailure) {
......
final ShardRouting shardRouting = shardIt.nextOrNull();
......
// 根据分片所在的节点ID从集群中的节点列表获取该节点,得到目标节点
DiscoveryNode node = nodes.get(shardRouting.currentNodeId());
// 如果节点为空抛出异常
if (node == null) {
onFailure(shardRouting, new NoShardAvailableActionException(shardRouting.shardId()));
} else {
// 目标分片的id
internalRequest.request().internalShardId = shardRouting.shardId();
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"sending request [{}] to shard [{}] on node [{}]",
internalRequest.request(),
internalRequest.request().internalShardId,
node
);
}
// 向目标节点转发请求
transportService.sendRequest(node, transportShardAction, internalRequest.request(), new TransportResponseHandler<Response>() {
public Response newInstance() {
return newResponse();
}
public String executor() {
return ThreadPool.Names.SAME;
}
public void handleResponse(final Response response) {
listener.onResponse(response);
}
public void handleException(TransportException exp) {
onFailure(shardRouting, exp);
}
});
}
}
TransportService
TransportService实现了sendRequest方法,在转发请求前,调用getConnection判断当前节点是否是目标节点:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25public class TransportService extends AbstractLifecycleComponent {
public <T extends TransportResponse> void sendRequest(final DiscoveryNode node, final String action,
final TransportRequest request,
final TransportResponseHandler<T> handler) {
try {
// 获取目标节点的连接
Transport.Connection connection = getConnection(node);
// 向目标节点发送请求
sendRequest(connection, action, request, TransportRequestOptions.EMPTY, handler);
} catch (NodeNotConnectedException ex) {
// the caller might not handle this so we invoke the handler
handler.handleException(ex);
}
}
public Transport.Connection getConnection(DiscoveryNode node) {
// 判断当前节点是否是目标节点
if (isLocalNode(node)) {
return localNodeConnection;
} else {
// 如果当前节点不是目标节点,获取目标节点的连接
return transport.getConnection(node);
}
}
}
数据节点
数据节点收到协调节点的请求,读取数据并返回Response,入口在TransportSingleShardAction.ShardTransportHandler的messageReceived方法中。
TransportSingleShardAction
TransportSingleShardAction.ShardTransportHandler的messageReceived是接收协调节点请求的入口:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public abstract class TransportSingleShardAction<Request extends SingleShardRequest<Request>, Response extends ActionResponse> extends TransportAction<Request, Response> {
private class ShardTransportHandler implements TransportRequestHandler<Request> {
@Override
public void messageReceived(final Request request, final TransportChannel channel) throws Exception {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("executing [{}] on shard [{}]", request, request.internalShardId);
}
// 读取数据并封装成Response
Response response = shardOperation(request, request.internalShardId);
// 发送响应
channel.sendResponse(response);
}
}
}
具体的读取过程:
TransportGetAction
TransportGetAction的shardOperation方法中调用了ShardGetService的get方法读取数据并存入GetResult中:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public class TransportGetAction extends TransportSingleShardAction<GetRequest, GetResponse> {
@Override
protected GetResponse shardOperation(GetRequest request, ShardId shardId) {
IndexService indexService = indicesService.indexServiceSafe(shardId.getIndex());
IndexShard indexShard = indexService.getShard(shardId.id());
// 检查是否需要refresh
if (request.refresh() && !request.realtime()) {
indexShard.refresh("refresh_flag_get");
}
// 调用ShardGetService的get方法读取数据并存入GetResult中
GetResult result = indexShard.getService().get(request.type(), request.id(), request.storedFields(),
request.realtime(), request.version(), request.versionType(), request.fetchSourceContext());
return new GetResponse(result);
}
}
ShardGetService
ShardGetService的get中又调用了innerGet方法,这里才是核心的数据读取实现:
1 | public final class ShardGetService extends AbstractIndexShardComponent { |
indexShard.get()方法返回的Engine.GetResult类型,在get方法中又调用了InternalEngine的get方法读取数据
IndexShard1
2
3
4
5
6public class IndexShard extends AbstractIndexShardComponent implements IndicesClusterStateService.Shard {
public Engine.GetResult get(Engine.Get get) {
readAllowed();
return getEngine().get(get, this::acquireSearcher);
}
}
InternalEngine
InternalEngine的get方法读取数据,在早期的ES版本中,刚写入的数据可以从translog读取,以此达到实时搜索,所以读取过程中会加锁,处理realtime选项,如果realtime为true,判断是否需要刷盘。ES 5之后不再从translog中读取,只从Lucene中读取,实时搜索依靠refresh实现。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33public class InternalEngine extends Engine {
@Override
public GetResult get(Get get, BiFunction<String, SearcherScope, Searcher> searcherFactory) throws EngineException {
assert Objects.equals(get.uid().field(), uidField) : get.uid().field();
// 加锁
try (ReleasableLock ignored = readLock.acquire()) {
ensureOpen();
SearcherScope scope;
// 处理realtime选项。判断是否需要刷盘
if (get.realtime()) {
VersionValue versionValue = versionMap.getUnderLock(get.uid().bytes());
if (versionValue != null) {
if (versionValue.isDelete()) {
return GetResult.NOT_EXISTS;
}
if (get.versionType().isVersionConflictForReads(versionValue.version, get.version())) {
throw new VersionConflictEngineException(shardId, get.type(), get.id(),
get.versionType().explainConflictForReads(versionValue.version, get.version()));
}
// 执行刷盘操作
refresh("realtime_get", SearcherScope.INTERNAL);
}
scope = SearcherScope.INTERNAL;
} else {
scope = SearcherScope.EXTERNAL;
}
// 调用searcher读取数据
return getFromSearcher(get, searcherFactory, scope);
}
}
}
数据节点读取流程总结:
- 数据节点接收到协调节点的请求读取数据
- 读取数据的核心实现是在ShardGetService的innerGet方法中实现的,在这个过程中,又依靠InternalEngine的get方法通过Searcher从Lucene中读取数据,然后innerGetLoadFromStoredFields方法对得到的数据进行过滤
- 数据节点将返回结果封装到Response中返回
参考:
Elasticsearch源码解析与优化实战【张超】
Elasticsearch版本:6.1.2